Table Of Content

The ship will sink if its weight is too great since the water displacement will never match the ship’s weight. Because cruise ships can shift water equivalent to their mass, they can float. Even the biggest cruise ships can float because of their hollow interior, low center of gravity, and U-shaped hull. With cruise ships testing the limits of height and weight, one must wonder what prevents them from capsizing. The answer to this question rests in the design of the hull.
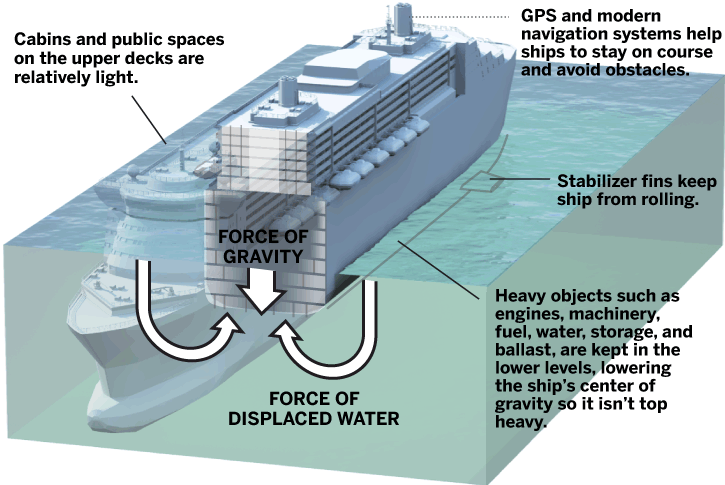
Two Forces Meeting
She has worked in the cruise industry since 2015 and has taken over 30 cruises. Now, she helps over 1 million people per month to plan their perfect cruise holidays. The science of buoyancy was discovered by Archimedes in 246 BC, when he developed Archimedes' principle. We’ll be sharing tips, advice, vlogs and the latest news on all of the biggest cruise lines. Terms and conditions apply to all offers and prices displayed on this website. Fares are subject to availability and operator booking conditions.
How Does a Ship Stay Standing Up?
This way, the hull can offer even more protection and give everybody peace of mind that the ship can remain stable and secure no matter what happens. Passengers on ships with these hull types rarely feel any rocking or side-to-side movement. Olsen are perfect for meandering along rivers and reaching narrow port openings, while larger ships like much of Royal Caribbean’s fleet are best suited for transatlantic sailings. Their size is much more relative to the body of water they’re floating on, which means they can be propelled upwards and remain steady as they sail. Maritime Page is your go-to source for all things related to the maritime industry, from personal watercraft to the largest seagoing cargo ships and cruise vessels. Cruise ships use a combination of stabilizers and advanced navigation systems to maintain stability in rough seas.
Weight and Volume
Round-bottom hulls move through the water and make them much more stable and seaworthy than a v-shaped boat hull. This is primarily why cruise ship passengers feel much less rocking or motion compared to a boat. Theoretically and practically, Archimedes’ Principle applies to huge cruise ships.
Not everything that's heavy sinks right to the bottom of the ocean floor, and there's no greater proof than Royal Caribbean's Wonder of the Seas, the biggest cruise ship on Earth. Whatever the case, the ship finally filled with water and sank. The ship’s average density increased as it filled with water until it was no longer able to float. The ship’s construction, size, kind of cargo, water density, and season all affect the depth.
Conversely, when the ship needs to be lightened, the water is pumped out of the tanks. This process helps to ensure that the ship remains stable and balanced, even in rough waters. The amount of water displaced by a ship is determined by its shape and size, as well as the density of the water.
Maritime Law: Murky Jurisdiction HowStuffWorks - People HowStuffWorks
Maritime Law: Murky Jurisdiction HowStuffWorks.
Posted: Thu, 29 Jun 2023 07:00:00 GMT [source]
The bottoms of cruise ships are not flat near the bow nor at the raised area at the stern where the propellors are. Most cruise ships also have bilge keels which also assist to limit the amount of roll. These are long, metal fins that are welded along each side of the ship. That’s why a strong wind hitting the side of the ship doesn’t tip it over. This is calculated as a wind heel moment and is a large part of the stability calculations for any vessel. Another major difference between a cruise ship and a boat is the design of the hull.
That’s why most cruise ships adopt a double hull design where one floater rests inside the other, serving as a backup if the outer piece punctures. Let’s go a little deeper and discover how objects like cruise ships manage to float. Aspects of their design, safety features, and other parts work with buoyancy to keep them upright even through the waves. When the density of an object is less than the density of water, the ship floats because the downward force of gravity is less than the upward force exerted by the liquid. A solid bar of steel dropped from a cruise ship balcony will undoubtedly sink until it reaches the bottom of the sea.
Cruise ships don’t capsize because of the materials used, which also keeps the ship lightweight. A ship floats when its density is lower than that of water because the upward pull of the liquid is greater than the downward force of gravity. After learning the fundamentals, let’s examine some of the physics underlying cruise ships’ ability to float. The largest cruise ship in the world weighs 236,857 tons and has 21 restaurants, 14 bars, three water slides, a mini golf course, and more. The larger the cruise ships have become, the more water they need to displace for them to be able to float.
The hull is typically made of steel, which is strong and durable enough to withstand the rigors of the open sea. The first thing you need to know about floating on water is that if something isn’t heavy enough to stay in place when submerged under water, then it will float away. A buoyant ship does exactly what a name suggests; it floats due to air trapped within the structure of the ship itself. These ships use ballast tanks filled with seawater and/or sand to keep themselves afloat. When these ballast tanks fill up with water, the ship sinks until the tank empties again. If you’ve ever seen a boat bobbing around in the ocean, chances are it was a buoyant ship.
What is more remarkable is learning how these modern marvels are equipped to float on water. When examining how cruise ships float, the answer truly lies in a mixture of scientific principles and design. Do you have any other tidbits to explain this scientific principle to cruise passengers? Drop us an anchor below to share your thoughts on the engineering marvels that are cruise ships.


No comments:
Post a Comment